张量#
简介#
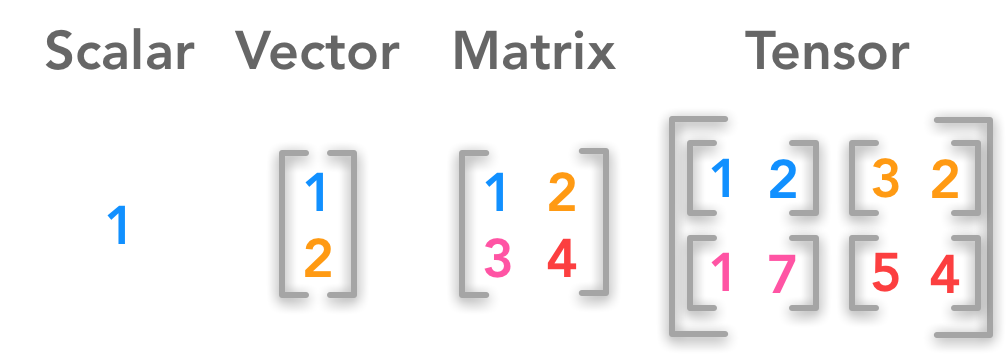
张量是一个数学的概念,任何维度都可以叫做张量,几何代数中定义的张量是基于向量和矩阵的推广,比如我们可以将标量视为零阶张量,矢量可以视为一阶张量,矩阵就是二阶张量。
张量维度 |
代表含义 |
|---|---|
0维张量 |
代表的是标量(数字) |
1维张量 |
代表的是向量 |
2维张量 |
代表的是矩阵 |
3维张量 |
时间序列数据 股价 文本数据 单张彩色图片(RGB) |
张量是现代机器学习的基础。它的核心是一个数据容器,多数情况下,它包含数字,有时候它也包含字符串,但这种情况比较少。因此可以把它想象成一个数字的水桶。
 这里有一些存储在各种类型张量的公用数据集类型:
这里有一些存储在各种类型张量的公用数据集类型:
3维 = 时间序列
4维 = 图像
5维 = 视频
例子:一个图像可以用三个字段表示:
(width, height, channel) = 3D
但是,在机器学习工作中,我们经常要处理不止一张图片或一篇文档——我们要处理一个集合。我们可能有10,000张郁金香的图片,这意味着,我们将用到4D张量:
(batch_size, width, height, channel) = 4D
在PyTorch中, torch.Tensor 是存储和变换数据的主要工具。如果你之前用过NumPy,你会发现 Tensor 和NumPy的多维数组非常类似。然而,Tensor 提供GPU计算和自动求梯度等更多功能,这些使 Tensor 这一数据类型更加适合深度学习。
创建tensor#
常见的构造Tensor的方法:
函数 |
功能 |
|---|---|
Tensor(sizes) |
基础构造函数 |
tensor(data) |
类似于np.array |
ones(sizes) |
全1 |
zeros(sizes) |
全0 |
eye(sizes) |
对角为1,其余为0 |
arange(s,e,step) |
从s到e,步长为step |
linspace(s,e,steps) |
从s到e,均匀分成step份 |
rand/randn(sizes) |
rand是[0,1)均匀分布;randn是服从N(0,1)的正态分布 |
normal(mean,std) |
正态分布(均值为mean,标准差是std) |
randperm(m) |
随机排列 |
张量运算示例#
import torch
查看版本
torch.__version__
'2.2.1+cpu'
查看该函数的解释
?torch.tensor
Docstring:
tensor(data, *, dtype=None, device=None, requires_grad=False, pin_memory=False) -> Tensor
Constructs a tensor with no autograd history (also known as a "leaf tensor", see :doc:`/notes/autograd`) by copying :attr:`data`.
.. warning::
When working with tensors prefer using :func:`torch.Tensor.clone`,
:func:`torch.Tensor.detach`, and :func:`torch.Tensor.requires_grad_` for
readability. Letting `t` be a tensor, ``torch.tensor(t)`` is equivalent to
``t.clone().detach()``, and ``torch.tensor(t, requires_grad=True)``
is equivalent to ``t.clone().detach().requires_grad_(True)``.
.. seealso::
:func:`torch.as_tensor` preserves autograd history and avoids copies where possible.
:func:`torch.from_numpy` creates a tensor that shares storage with a NumPy array.
Args:
data (array_like): Initial data for the tensor. Can be a list, tuple,
NumPy ``ndarray``, scalar, and other types.
Keyword args:
dtype (:class:`torch.dtype`, optional): the desired data type of returned tensor.
Default: if ``None``, infers data type from :attr:`data`.
device (:class:`torch.device`, optional): the device of the constructed tensor. If None and data is a tensor
then the device of data is used. If None and data is not a tensor then
the result tensor is constructed on the current device.
requires_grad (bool, optional): If autograd should record operations on the
returned tensor. Default: ``False``.
pin_memory (bool, optional): If set, returned tensor would be allocated in
the pinned memory. Works only for CPU tensors. Default: ``False``.
Example::
>>> torch.tensor([[0.1, 1.2], [2.2, 3.1], [4.9, 5.2]])
tensor([[ 0.1000, 1.2000],
[ 2.2000, 3.1000],
[ 4.9000, 5.2000]])
>>> torch.tensor([0, 1]) # Type inference on data
tensor([ 0, 1])
>>> torch.tensor([[0.11111, 0.222222, 0.3333333]],
... dtype=torch.float64,
... device=torch.device('cuda:0')) # creates a double tensor on a CUDA device
tensor([[ 0.1111, 0.2222, 0.3333]], dtype=torch.float64, device='cuda:0')
>>> torch.tensor(3.14159) # Create a zero-dimensional (scalar) tensor
tensor(3.1416)
>>> torch.tensor([]) # Create an empty tensor (of size (0,))
tensor([])
Type: builtin_function_or_method
创建tensor
用dtype指定类型。注意类型要匹配,如果不同类型的话会被强制转换,可以参考c变量从float类型被强制转换成了int8类型
a = torch.tensor(1.0, dtype=torch.float)
b = torch.tensor(1, dtype=torch.long)
c = torch.tensor(1.0, dtype=torch.int8)
print(f"a:{a}")
print(f"b:{b}")
print(f"c:{c}")
a:1.0
b:1
c:1
使用指定类型函数随机初始化指定大小的tensor
PS:如果是以前的版本会生成随机数的浮点类型,而不是都为0的浮点类型
d = torch.FloatTensor(2,3)
e = torch.IntTensor(2)
f = torch.IntTensor([1,2,3,4]) #对于python已经定义好的数据结构可以直接转换
print(f"d:{d}")
print(f"e:{e}")
print(f"f:{f}")
d:tensor([[-2.3352e-33, 1.3747e-42, 0.0000e+00],
[ 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00]])
e:tensor([0, 0], dtype=torch.int32)
f:tensor([1, 2, 3, 4], dtype=torch.int32)
Tensor和numpy array之间的相互转换
import numpy as np
g = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
h = torch.tensor(g)
print(f"h:{h}")
i = torch.from_numpy(g)
print(f"i:{i}")
j = h.numpy()
print(f"j:{j}")
h:tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]], dtype=torch.int32)
i:tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]], dtype=torch.int32)
j:[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
注意:torch.tensor创建得到的张量和原数据是不共享内存的,张量对应的变量是独立变量。
而torch.from_numpy()和torch.as_tensor()从numpy array创建得到的张量和原数据是共享内存的,张量对应的变量不是独立变量,修改numpy array会导致对应tensor的改变。
g[0,0] = 100
print(f"i:{i}")
i:tensor([[100, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]], dtype=torch.int32)
常见的构造Tensor的函数
k = torch.rand(2, 3) #随机生成维度为2,3的张量
l = torch.ones(2, 3) #全1的张量
m = torch.zeros(2, 3) #全0的张量
n = torch.arange(0, 10, 2) #用于创建一个一维张量,其中包含一个等差数列,(初始值,结束值,步长)
print(f"k:{k}")
print(f"l:{l}")
print(f"m:{m}")
print(f"n:{n}")
k:tensor([[0.7292, 0.8921, 0.3807],
[0.0924, 0.6564, 0.5757]])
l:tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
m:tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]])
n:tensor([0, 2, 4, 6, 8])
查看tensor的维度信息(两种方式)
print(f"k.shape:{k.shape}") #标准用法是这个
print(f"k.size():{k.size()}")
k.shape:torch.Size([2, 3])
k.size():torch.Size([2, 3])
tensor的加法运算
# 方法1
o = torch.add(k,l) #两个张量相加,两个张量必须具有相同的形状,(输入张量,要相加的张量)
print(f"o:{o}")
# 方式2
print(f"k + l:{k + l}")
o:tensor([[1.7292, 1.8921, 1.3807],
[1.0924, 1.6564, 1.5757]])
k + l:tensor([[1.7292, 1.8921, 1.3807],
[1.0924, 1.6564, 1.5757]])
tensor的索引方式
tensor的索引方式与numpy类似,需要主要的是:表示取该维度全数据,如果是x:y表示取该维度上[x,y)之间的数据,而单独一个数据就是维度了比如1就表示取该维度上[1,1]之间的数据。
print(f"o[:,1]:{o[:,1]}")
print(f"o[0:1,1]:{o[0:1,1]}")
print(f"o[0,:]:{o[0,:]}")
o[:,1]:tensor([1.8921, 1.6564])
o[0:1,1]:tensor([1.8921])
o[0,:]:tensor([1.7292, 1.8921, 1.3807])
改变tensor形状的神器:reshape
print(f"o.reshape(3,2):{o.reshape(3,2)}")
print(f"o.reshape(-1,2):{o.reshape(-1,2)}")
o.reshape(3,2):tensor([[1.7292, 1.8921],
[1.3807, 1.0924],
[1.6564, 1.5757]])
o.reshape(-1,2):tensor([[1.7292, 1.8921],
[1.3807, 1.0924],
[1.6564, 1.5757]])
tensor的广播机制(使用时要注意这个特性)
当对两个形状不同的 Tensor 按元素运算时,可能会触发广播(broadcasting)机制:先适当复制元素使这两个 Tensor 形状相同后再按元素运算。
p = torch.arange(1, 3).reshape(1, 2)
print(f"p:{p}")
q = torch.arange(1, 4).reshape(3, 1)
print(f"q:{q}")
print(f"q+p:{q+p}")
p:tensor([[1, 2]])
q:tensor([[1],
[2],
[3]])
q+p:tensor([[2, 3],
[3, 4],
[4, 5]])
扩展tensor的维度:
torch.unsqueeze 是一个函数,用于在张量的指定位置插入一个维度。它的语法如下:
torch.unsqueeze(input, dim)
其中,参数的含义如下:
input:输入张量。dim:要插入新维度的位置。
print(f"o.shape:{o.shape}")
r = o.unsqueeze(1)
print(f"r:{r}")
print(f"r.shape:{r.shape}")
r_ = o.unsqueeze(2)
print(f"r_.shape:{r_.shape}")
o.shape:torch.Size([2, 3])
r:tensor([[[1.7292, 1.8921, 1.3807]],
[[1.0924, 1.6564, 1.5757]]])
r.shape:torch.Size([2, 1, 3])
r_.shape:torch.Size([2, 3, 1])
压缩tensor的维度:
torch.squeeze 是一个函数,用于从张量中删除尺寸为 1 的维度,如果维度的尺寸不为 1 那么就不做任何处理。它的语法如下:
torch.squeeze(input, dim=None, out=None)
其中,参数的含义如下:
input:输入张量。dim:要删除的维度的索引或名称。如果指定了dim,则只删除指定的维度。如果未指定dim,则删除所有尺寸为 1 的维度。out:输出张量,可选参数。
torch.squeeze 将从输入张量 input 中删除尺寸为 1 的维度,并返回结果。如果指定了 dim,则只删除指定的维度。如果未指定 dim,则删除所有尺寸为 1 的维度。
以下是一个示例:
import torch
x = torch.tensor([[[1, 2, 3]]])
print(x.shape) # 输出: torch.Size([1, 1, 3])
y = torch.squeeze(x)
print(y.shape) # 输出: torch.Size([3])
z = torch.squeeze(x, dim=0)
print(z.shape) # 输出: torch.Size([1, 3])
在上面的示例中,我们首先创建了一个形状为 (1, 1, 3) 的三维张量 x。然后,我们使用 torch.squeeze 删除了 x 中的尺寸为 1 的维度,得到了形状为 (3,) 的一维张量 y。接下来,我们使用 torch.squeeze 删除了 x 中的第一个维度(即位置 0)的尺寸为 1 的维度,得到了形状为 (1, 3) 的二维张量 z。
print(f"r:{r}")
print(f"r.shape:{r.shape}")
s = r.squeeze(0) #维度不为1所以不做任何处理返回结果不变
print(f"s:{s}")
print(f"s.shape:{s.shape}")
r:tensor([[[1.7292, 1.8921, 1.3807]],
[[1.0924, 1.6564, 1.5757]]])
r.shape:torch.Size([2, 1, 3])
s:tensor([[[1.7292, 1.8921, 1.3807]],
[[1.0924, 1.6564, 1.5757]]])
s.shape:torch.Size([2, 1, 3])
t = r.squeeze(1)
print(f"t:{t}")
print(f"t.shape:{t.shape}")
s:tensor([[[1.7292, 1.8921, 1.3807]],
[[1.0924, 1.6564, 1.5757]]])
s:tensor([[[1.7292, 1.8921, 1.3807]],
[[1.0924, 1.6564, 1.5757]]])
tensor([[1.7292, 1.8921, 1.3807],
[1.0924, 1.6564, 1.5757]])
torch.Size([2, 3])
t_ = r.squeeze() #不填内容,就删除所有的维度为1的
print(f"t_:{t_}")
print(f"t_.shape:{t_.shape}")
t_:tensor([[1.7292, 1.8921, 1.3807],
[1.0924, 1.6564, 1.5757]])
t_.shape:torch.Size([2, 3])